Definition
Offshore outsourcing is the practice of hiring an external organization to perform some business functions (Outsourcing) in a country other than where the products or services are actually developed or manufactured (Offshore).
In the unforgettable freeway action scene in “Terminator 2: Judgement Day”, Arnie saves John Connor atop of a Harley-Davidson ‘Fatboy’ as he snatches the kid off a dirt bike that is about to be crushed by a monster truck driven by the new T-1000 Terminator.
Harley’s are an absolute icon of U.S. manufacturing, about as American as apple pie. Along with T2, they also feature in the 60’s classic, “Easy Rider”, and Quentin Tarantino’s “Pulp Fiction”. It’s hard to imagine the celebrated machines being built anywhere else except in a mid-west wilderness where men get drunk on Buds (Budweiser beer), after pouring their blood, sweat and tears into making the legendary Chopper bikes.
However, Harley-Davidson Inc., which is based in Milwaukee, has been offshoring for a number of years, having opened factories in Brazil, India and Australia. When it announced last June plans to shift production of its EU-targeted motorcycles (in response to tit-for-tat trade tariffs) the company came into the crosshairs of President Donald Trump, who threatened to hike taxes on the manufacturer when it sold back into the country. This proves that offshore outsourcing is a pretty hot topic.
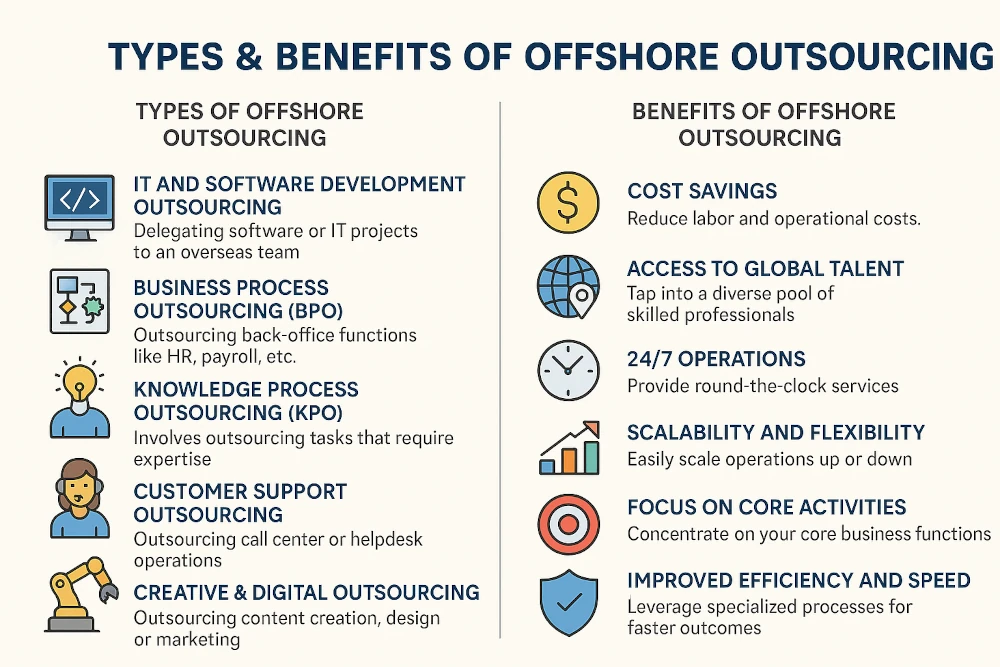
Types of Offshore Outsourcing
1. Production Offshoring
Also known as Business Process Outsourcing (BPO), this involves the actual relocation of the physical manufacturing process overseas, usually at a much lower cost in terms of labour and materials. The range of offshored processes and functions can be subdivided into two main categories; front-office and back-office solutions. The former includes things like customer service support (call centres, help desks), inbound/outbound telemarketing, virtual assistants and technical support. Many businesses find strategic advantages in call center outsourcing to streamline their customer interaction processes while reducing operational costs. The latter concerns processes like HR and recruitment, accounting and bookkeeping, mobile and web development and design and graphics.
2. System Services Offshoring
Given the multitude of processes and minute-by-minute tasks of any business operation, information technology (IT) is going to be a key concern to get right. In the 1990s the availability of large amounts of communication infrastructure helped countries like India, with its large pool of English speakers and technically proficient workforce; lead the field by attracting firms like HP, IBM, Microsoft, Oracle Corporation, Intel and Cisco.
Exploring offshore bpo services can provide your business with cost-effective and efficient solutions for various operational needs.
When managing IT functions becomes overwhelming, consider optimizing your workflow by hiring a virtual assistant. A virtual assistant can handle various administrative tasks, allowing you to focus on strategic aspects of your business and enhance overall productivity.
3. Innovation and Software Offshoring
Asian countries lead the world in computer science and software development services. However, many high-tech product companies, like those in Silicon Valley, have started offshoring innovation work to countries such as Colombia, Belarus, South Africa, Mexico and Ukraine. Accessing the highly-skilled talent pools in these countries offers significant cost savings and shorter production cycles.
4. Reshoring
Also known as backshoring or inshoring, essentially offshoring that comes back. Companies like Google, Facebook and Amazon, have been heavily criticised in European quarters for alleged concealment of income and tax avoidance by using low-tax havens like the Republic of Ireland to book non-US revenues from large advertisers through its Dublin unit. As a result, it announced in January 2018 that it would book those revenues in the countries where they were earned and pay the taxes on those revenues in those countries.
Recommended for you:
In 2025 Outsource Software Development to These Countries in Asia
Benefits of Offshore Outsourcing
- Cheaper Labour Costs
Obviously, the cost of living in developing countries in Asia or under-developed Eastern bloc territories where benefit systems and legal wages may not be a factor can help to significantly boost a firm’s profits. However, that can be an exploitative outcome that in the long run could damage a company’s reputation, especially in the enlightened times we live in.
- Skilled and Motivated Workforce
One of the reasons why companies outsource is because they intend to utilize the opportunity to get the skilled resource on board and take their respective firms to new heights. The human resources, on the other hand, also remain motivated due to the sense of accomplishment they feel while working for a reputable foreign firm.
- Speed and Efficiency
When you have a big project in-house it can get stuck in the mud. Often a fresh approach, new eyes and energy can help to cut through the fog, especially if it needs to be delivered on a super-tight deadline.
Outsourcing the workforce in business, especially on the technological side of the business is quite challenging. Ratcliff IT London provides comprehensive IT solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of businesses, ensuring seamless integration of technology while allowing companies to focus on their core operations. From managed IT services to cybersecurity, Ratcliff IT London offers expert support that enhances productivity and reduces the burden of in-house IT management.
- Less Regulative Obstacles
With a mountain of legal regulations and procedural paperwork to overcome, doing business can mire you in red tape. Companies will sometimes opt for an environment where they feel they can move faster and get their product out quicker in the highly competitive markets they work in.
- Allows Concentration on Core Businesses
If you’re running a restaurant you don’t want to be the chief cook and the bottle washer. It might pay to hire someone to do some of the smaller tasks. For example, a manager becomes a marketer ― but what do they know about marketing? Learning curves are time-consuming and can be an inefficient use of time. Outsourcing gets you access to expertise – and since the task you pass on to them is the core business of the organizations to which you outsource, they should be on top of the game. There’s no wait time or down-prioritizing. They want to get paid and will be just as keen to see the job done.
Examples of Offshoring
1. Nike
Like its most famous brand endorser ‘His Airness’ Michael Jordan, the Swoosh is a big player in the offshore outsourcing game.
When Nike, Inc. was founded in 1964 by entrepreneur Phil Knight and former athletic coach William Jay “Bill” Bowerman, just four percent of U.S. footwear was imported. Today that figure is a staggering 98 percent, led by the vision of Knight, who according to the Wall Street Journal came up with the idea of outsourcing manufacturing jobs to cut costs while attending Stanford Business School in the early 1960s.
The company, valued at £29.6 billion by Forbes Magazine, has a manufacturing network of over 700 factories in 42 countries, yet it does not own any of these facilities. The entire footwear and apparel brand is sourced to independent contract manufacturers that often operate multiple factories. According to the most recent fiscal reports, Nike footwear was supplied by 150 factories in 14 countries. Meanwhile, 430 factories in 41 countries supplied its apparel lines.
2. Amazon
The clue’s probably in its name, but Amazon.com Inc. didn’t become the first trillion dollar company ― making its founder Jeff Bezos the richest person in the world ― without taking advantages of foreign economies of scale.
The company has morphed from debuting as an online bookseller in 1994 to offering a dizzying array of products and services in multi-media, technology, retail and groceries. Its distribution and fulfilment network can be found in Europe, Asia, Africa South America and Oceania.
EnamelPins Inc. is a cross-border e-commerce independent platform operating company that aspires to build national independent brands to go overseas. The platform market is currently dominated by Europe, America, Australia, and other British countries, mainly engaged in all kinds of customized advertising promotional products, and souvenirs, such as custom patches, custom pins, custom medals, and other products.
The Group has 4 wholly owned factories located in Kunshan and Changde, China. Currently, the group has its physical operation subsidiaries in Los Angeles, USA, and Vancouver, Canada, and its ultimate goal is to build a 24-hour online service network covering the whole world.
Conclusion
With every nook and cranny of our world at the mercy of the irresistible forces of offshoring and outsourcing, are there any more foreign territories for these Wall Street superstars to conquer? Well, in the week that NASA (The National Aeronautics and Space Administration) announced plans for humans to return to the Moon by 2024, that future could literally be in the stars.


